Urine Infection kya hai: Urinary tract infections are among many common conditions responsible for frequent doctor visits. UTIs affect all age groups including children, adult men and women and elderly people. About 150 million cases of urinary tract infections are recorded every year all over the world.
Types of urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infections can be complicated, uncomplicated and asymptomatic on the basis of symptoms and severity of the infection.
- Uncomplicated urinary tract infection
This type of UTI is seen in healthy people who do not have any underlying structural abnormalities (such as blockages or abnormal growth) or neurological conditions (related to the nervous system) in their urinary tract which could make them prone to UTI. - Complicated urinary tract infections
This type of infection occurs in people who have an underlying condition such as an obstruction or blockage in the urinary system, neurological problems of the urinary tract that cause collection or retention of the urine, kidney failure or transplant, a weak immune system, kidney (renal) stones, a catheter in the bladder (indwelling catheter), elderly people and women who are pregnant. - Asymptomatic bacteriuria
It is the condition in which a person has an infection but there are no symptoms of UTI. Although healthy people could get this type of UTI, it is common in adult women, especially those who are pregnant or approaching menopause, people with diabetes, a catheter in the bladder, spinal cord injury, and elderly people. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is generally diagnosed after urine analysis because of the absence of symptoms.
Also Read : Lost Interest in Sex? Know Reasons of Decreasing Sex Power
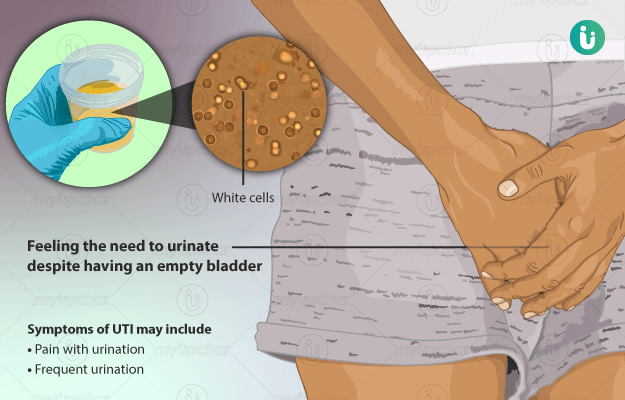
Urinary tract infection (UTI) symptoms
The infection-causing bacteria enter the urinary system through the urethra, attack the inner lining of the urinary tract and depending on the location (bladder, urethra, kidneys) that is prone to bacterial growth and multiplication. Uncontrolled growth of bacteria causes inflammation and redness along with various other symptoms such as:
- Burning sensation or pain while passing urine, chiefly due to irritation in the urinary bladder.
- Pain in the lower abdomen is also associated with a burning sensation while urinating due to bladder inflammation.
- Sudden urge to pass urine when the bladder is empty or after passing urine.
- Occasionally, the person may also lose control of urine.
- Frequent sensation or urge to pass urine.
- Bad urine odour.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) causes and risk factors
Causes
Various bacteria and fungi are responsible for causing infections in the urinary tract. Some of the most common ones include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumonia, Enterococcus faecalis, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
Risk Factors
Multiple risk factors can increase a person’s risk of getting urinary tract infections. These differ in males and in females and include:
Risk factors in males
- Obstruction or blockage in the urinary tract after the use of instruments (for dilating a narrowed urethra), a catheter in the urinary bladder or surgery of the urinary tract.
- Enlarged prostate gland results in an incomplete blockage of the urinary tract which leads to the development of urinary infections in men above 50 years of age.
- Use of catheter in men with diabetes.
- Men are older than 50 years of age.
- Acute UTIs (such as acute cystitis) are common in homosexual young men, men who have unprotected sex with an infected female partner, HIV positive men, and more.
Also Read : Diet during periods- Important things to notice
Prevention of urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infections can be prevented to some extent by following certain precautions in day-to-day life. Here are some ways that can help you in staying away from UTIs:
- Drink 1-2 litres of water to hydrate your body adequately and avoid recurrent UTIs.
- Limit the intake of alcohol and caffeinated drinks as they cause irritation of the inner lining of the urinary bladder.
- Make sure that you pass urine right before and after having sex to prevent UTI.
- Avoid bath oils or bubble baths. Bathing under running water like showers is more effective in cleaning the body than taking bath in a tub.
- Avoid using tight-fitting inner wears. Cotton undergarments are better than synthetic ones.
- Opt for sanitary pads instead of tampons. Sanitary pads instead of tampons decrease the risk of urinary tract infections.
- Avoid use of spermicide foam or spray as a contraceptive on the genital area as it increases the risk of urinary tract infection.
- Urinary catheters should not be kept in place beyond the required duration.
Read more:Sex during periods leads to pregnancy? All you need to know
