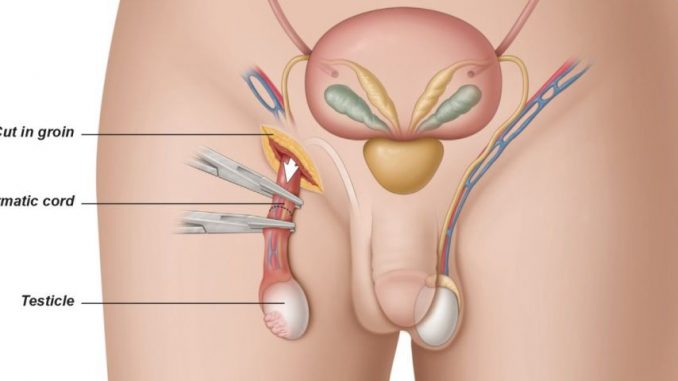
Doctors prefer to perform radical inguinal orchiectomies rather than biopsy the testicles because a biopsy can spread cancer. In a radical inguinal orchiectomy, the testis and tumor are also removed along with the testicular tube, so this surgery is called a ‘radical’. This tube contains blood and lymph vessels that can spread cancer to other parts of the body.
In simple orchiectomy, doctors remove only one or both testicles. These Males have 2 testicles that are egg-shaped and are about 5 cm long. They are the major part of the reproductive system of males that are covered by the scrotum. There is a scrotum under the penis between the two legs. Sperm are formed in the testicles only. They also make testosterone, which is the male sex hormone. The first treatment to eradicate a tumor in any testicle is a high inguinal orchiectomy (surgery performed by making a small incision down the side of the abdomen). Further treatment depends on the stage of the disease and the risk thereafter.
Also Read – What is Sperm Production : How to Increase it Each Day?
What is Orchiectomy?
Surgery performed to remove one or both testicles (testes) is called an orchiectomy. These surgeries are usually performed to treat prostate cancer or prevent it from spreading. Orchiectomy can treat testicular cancer and breast cancer in men. On the other hand, if a man wants to change his gender, then in this situation, orchiectomy surgery is also done to make the man a woman before sexual reassurance surgery (SRS).
There are many types of orchiectomy surgeries and depending on the condition of the patient it is decided which type of orchiectomy surgery to be performed.
-
Simple orchiectomy:
In this, one or both testicles are removed by making a small cut in the testicle. These surgeries are done when the doctor has to limit the amount of testosterone produced in the body in case of breast cancer or prostate cancer.
-
Radican inguinal orchiectomy:
In this surgery, one or both testicles are removed by making a small cut in the lower abdomen instead of the testicle. This surgery is performed in cases where there is a lump in the testicle and if the doctor wants to check for cancer in the testicle. Doctors may use this surgery to check for cancer as regular tissue samples or biopsies are more likely to spread cancer cells. This surgery is also a better way for men to become women
-
Subcapsular orchiectomy:
These surgeries are performed to remove the testicular tissue around the testicle from the testicle. There is no need to remove the testicle and looking from outside, it is also not known that something has been removed from this part.
-
Bilateral orchiectomy:
In this, both testicles are removed. These surgeries can be done in the event of prostate cancer, breast cancer or from male to female.
Why is the operation of testicles done?
This surgery is usually done to treat testicular cancer, but if any injury or infection has caused damage to the testes or testicles, then this surgery can be done in this situation too. Sometimes this prostate can also be a part of cancer treatment.
If the doctor suspects testicular cancer, they can ask for an ultrasound test to know what the patient is suffering from. Surgery helps in improving the symptoms of prostate cancer, causing problems, and treating breast cancer in men.
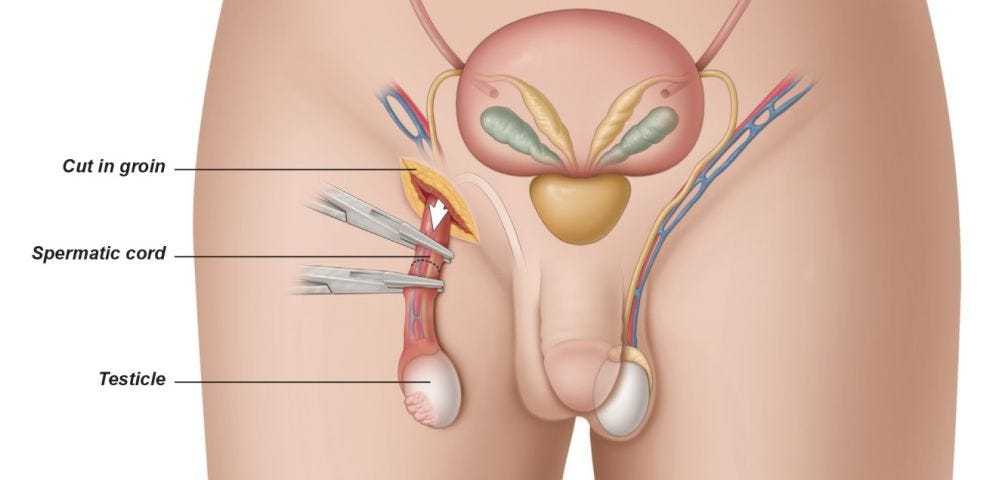
How is the testicle surgery done?
During the surgery, the surgeon first lifts the penis and affixes it to the abdomen via tape. They then make an incision on the scrotum or lower abdomen just above the pubic bone (the bone in front of the pelvis between the abdomen and thighs). Now one or both testicles are cut from the surrounding tissues and vessels and removed through the incision.
Surgeons will use clamps to stop blood flow from the sperm duct. Now the surgeons replace the removed testicles with fake or artificial testicles. The surgeon then cleanses this part with a saline solution (saltwater) and closes the incision with stitches.
Do’s and don’ts after orchiectomy:
- After surgery, apply ice to reduce swelling of the scrotum. This will give you rest in a few days. Do not ice for more than 15 minutes at a time.
- Surgeons may ask you to wear a jockstrap or tight underwear for a few days to reduce swelling.
- Take all medicines prescribed by your doctor. Do not start driving until the medicine is stopped and without asking the doctor.
- Your doctor will tell you when to start bathing. Avoid bathing and swimming until the surgical wound is healed.
- Ask the doctor about how to care for and clean the incision area. Check for infection or any other problem in this area daily.
- Rest for a few days after surgery. Do not lift, do sex, and do any hard exercises for a few weeks. Pay attention to everything the doctor says and instructions.
- If you have had this surgery due to cancer, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be needed to prevent the remaining cancer cells from spreading.
- Keep the wound area clean and dry.
- Apply a cream or ointment as advised by your doctor.
- One can take pain-relieving drugs like ibuprofen to reduce pain.
- Do not force too much during bowel movements. Drink plenty of water and take a fiber-rich diet to avoid constipation. You can also take medicine or powder to thin the stool.
- It may take between two weeks to two months to fully recover after orchiectomy surgery.
